The web can be broken down into three parts: the surface web, the deep web, and the dark web. The surface web includes anything you can find by entering terms into a search engine like Google. All the websites you visit that don’t require login credentials or specialist software are part of the surface web.
Beyond that lie the deep and dark parts of the web.
Dark web vs. deep web: What are they?
The key difference between the deep web and the dark web is that the deep web refers to all web content that requires login credentials to access, while you need special software to reach dark web content.
The dark web is just one part of the deep web. Normal sites on the deep net (like your online banking site or email account) sit behind secure logins, paywalls, passwords, and authentication forms, but you don’t need any special software to reach them. By contrast, to access darknet websites, you need special tools or software like Tor Browser.
The dark web is so named because of its hidden configurations, its emphasis on anonymity, and the private activity that happens there. The “deep” in deep web simply refers to the fact that you need passwords or other authentication to unlock it.
The rest of the web is known as the surface web.
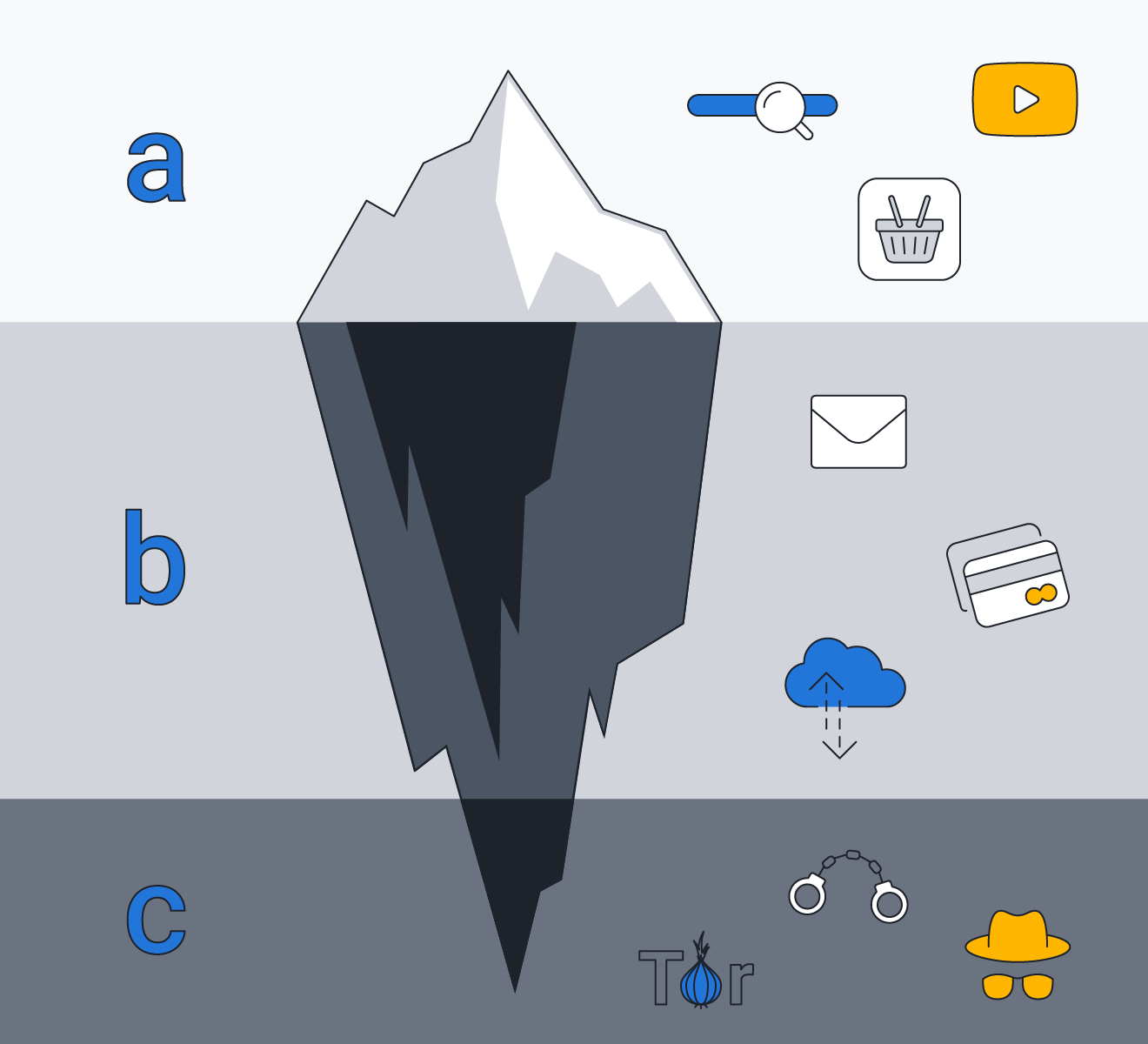 A: The surface web contains publicly accessible websites.
A: The surface web contains publicly accessible websites.
B: The deep web includes sites that require logins.
C: The dark web contains non-indexed sites that require special tools to access.
Is the dark web safe?
It’s usually safe to access the dark web. But just like when you’re online normally, the risks increase depending on what you do while visiting dark web websites. For example, it’s dangerous to buy or download anything from illegal marketplaces — the downloaded files may contain malware and the police can trace illegal purchases.
How to stay safe on the dark web
To stay safe on the dark web, use privacy tools, practice caution when choosing which sites to visit, and avoid transactions. This will help to protect you from malicious sites designed to steal your data or money.
Follow these dark web safety tips to help keep yourself and your information safe:
-
Use a VPN: Using a reliable VPN is essential for helping to keep your activity hidden on the dark web by masking your IP address. But it’s not enough to use a VPN on its own.
-
Use burner accounts: Create temporary accounts with as little similarity to your usual login credentials as possible. Avoid using any information such as passwords, usernames, and emails that are associated with accounts you have on the surface web.
-
Don’t use admin logins: Use a local profile on your device rather than an admin account. This will restrict certain permissions and help contain hacking attacks should the worst happen.
-
Use antivirus software: Robust antivirus software can help protect your devices against the malware and viruses that lurk across the dark web.
-
Be cautious: Don’t download files or click links unless you know the source is trustworthy. It’s always better to be safe than sorry, so if something doesn’t look right, it probably isn’t.
-
Avoid transactions: The dark web is a hotbed for scammers of all kinds, so don’t purchase anything if you’re not 100% sure that the seller is legitimate. If you fall victim to a scam, you may not be able to get your money back, especially if you use cryptocurrency.
-
Cover your webcam: It’s possible for skilled dark web hackers to gain access to your webcam. Cover your camera to help prevent spying, and get an anti-hacking tool to help protect your webcam against hackers.
-
Enhance your privacy options: Disabling JavaScript, ActiveX, and Flash plugins on your browser can help prevent certain harmful pop-ups or website elements from appearing. However, keep in mind that some sites also won’t display legitimate content fully without these features enabled.
Benefits of the dark web
The biggest benefit of the dark web is its extreme online privacy — much of the dark web isn’t shady, illegal, or used for criminal purposes. Dark web browsing is often motivated by the desire to keep your real identity secure and your online activity private.
Browser fingerprinting and online tracking are virtually impossible when you’re connected to the dark web via Tor Browser. That means your browsing behavior and traffic patterns can’t be collected and sold by data brokers or used by third-party advertisers.
Why does the dark web exist?
There are many legitimate reasons why the dark web exists: anonymous browsing, accessing research or other content without paywalls, discovering old or hard-to-find texts, and visiting special forums or social media websites.
Privately connecting to the dark web helps to avoid censorship and get around content blocks. And where access to popular social media or news sites is censored, dark web links to the same sites can help you stay informed.
The New York Times and Facebook both have dark web versions. Whistleblowers, journalists, and activists also use dark web tools — especially if they live in countries with repressive political regimes. The dark web has been vital for social change and market decentralization.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are also widely traded on the dark web. These transactions occur without a centralized bank, which means no standard form of personal information is necessary.
Dark web services
The dark web offers a number of services such as torrenting, crypto exchanges, and marketplaces. There are many dark web search engines that can be used with Tor Browser, including Torch, Haystack, and Not Evil, to help you navigate to different sites and services.
Services that can be found on dark web websites include:
-
Access to paywalled content: Dark web websites like Sci-Hub offer free access to thousands of academic papers that are hidden behind paywalls on the surface web.
-
News websites: The dark web contains accessible versions of news websites like the BBC and The New York Times, which are often accessed by people in countries with high levels of government censorship.
-
Social media: The dark web also offers versions of mainstream social media websites like Facebook and TikTok that can be accessed without government restrictions.
-
Crypto services: Cryptocurrency was born on the dark web, with the likes of Bitcoin kicking things off back in 2009. Cryptocurrency is used to purchase a variety of goods across the dark web. Crypto exchanges like Coinbase allow users to buy and sell various cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
-
Torrenting sites: Torrenting involves downloading or accessing content like films, music, and software via a peer-to-peer (P2P) sharing network. While torrenting itself isn’t illegal, the content you access may be copyrighted and illegally pirated.
-
Dark web wikis: Dark web wikis, such as The Hidden Wiki, act as an indexes, providing thousands of links to other dark web websites.
-
Dark web marketplaces: The dark web offers a great way to shop online anonymously. There are plenty of legitimate businesses selling on dark web marketplaces, although criminals also navigate these sites as well. The now-defunct dark web site Silk Road is a famous example of a marketplace where illegal purchases (weapons, drugs, data, etc.) were common.
-
Whistleblowing services: Sites like Secure Drop allow whistleblowers to send materials to high-profile media outlets securely. The Guardian, the Intercept, the Washington Post, and The New York Times are just some of the prominent media organizations that use Secure Drop.
Many of these services are legal and legitimate, but they can host illegal content or activity. Practice caution when interacting with dark web services to stay protected and on the right side of the law.
Is it illegal to access the dark web?
Depending on where you are, accessing the dark web might be illegal. But unless you engage in illegal activity on the dark web, you shouldn’t need to worry — at least in the US. Connecting to the dark web might draw unwelcome attention to your online activity, though, either from your internet service provider (ISP) or your government.
There are countries where access to the dark web is restricted by the government. For example, China blocks the Tor network IP addresses using the “Great Firewall”, and the Russian government has urged Internet Service Providers to block access to the Tor network. However, determined users may find workarounds.
If you do access the dark web, use a VPN so that your connection is encrypted. And check your local laws to find out if accessing the dark web is legal. These laws should cover what you need to know about using a VPN, proxy server, or Tor Browser to connect to the internet. To learn more, check out our guide to the best VPN server countries to connect to.
While it’s not illegal in many places to simply get on the dark web, the dark web is used for some illegal purposes. Many items and services for sale on dark web marketplaces are illegal, like ransomware or other strains of malware, illicit drugs, weapons, and, in some cases, human organs.
 All kinds of illegal goods may be for sale on dark web marketplaces.
All kinds of illegal goods may be for sale on dark web marketplaces.
What can you buy on the dark web?
You can buy a wide range of legal goods and services on dark web marketplaces. There are also some illegal things for sale, as detailed in the Dark Web Price Index 2023. If you decide to take the risk and make legal purchases on the dark web, protect yourself by using anonymized account information and cryptocurrency whenever possible.
Are my details on the dark web?
If your details have been exposed in a data breach it’s possible that they’re on the dark web. And once they’re listed there, it’s nearly impossible to remove them. Websites like Have I Been Pwned can scan the surface web and detect whether you’ve been the victim of a data breach, and you can set up a Google monitoring profile and run dark web report that alerts you if your information is on the dark web.
Or, you can scan the dark web using a trusted software like AVG Breach Guard.
If a website you have an account with gets hacked, AVG Breach Guard sends you an alert. What’s more, if we detect that hackers have exposed your personal information on the dark net, we can spot it and send you a notification, allowing you to act fast and keep you safer against identity theft.
Types of threats on the dark web
Though visiting the dark web is generally safe, you can still encounter threats such as scams, spyware, and identity theft. Browsing the dark web is riskier than browsing the surface web because it’s usually difficult to assess website safety. And without experience deciphering trustworthy dark web sites, it’s easy to fall prey to dangerous cybercriminals.
Here are some common types of threats on the dark web:
-
 Malware: Most of the world’s malware is sold and distributed on the dark web. Before you browse the dark web, install a free malware removal tool to detect malware attacks and protect your system from infection.
Malware: Most of the world’s malware is sold and distributed on the dark web. Before you browse the dark web, install a free malware removal tool to detect malware attacks and protect your system from infection.
-
 Scams: Due to unregulated transactions on the dark web, scams are everywhere. The same privacy that hides your activity on the dark web also makes it easy to carry out fraud. Stolen credit card numbers that result from data breaches often end up for sale on the dark web.
Scams: Due to unregulated transactions on the dark web, scams are everywhere. The same privacy that hides your activity on the dark web also makes it easy to carry out fraud. Stolen credit card numbers that result from data breaches often end up for sale on the dark web.
-
 Spyware: Spyware like the XKEYSCORE spy program — famously revealed by NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden — is still a security issue for Tor users and visitors to the dark web.
Spyware: Spyware like the XKEYSCORE spy program — famously revealed by NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden — is still a security issue for Tor users and visitors to the dark web.
-
 Identity theft: Scammers on the dark web might trick you into hasty purchases or disclosing personal information so they can collect your data and use it against you. Encrypt your connection and use pseudonyms and cryptocurrency to avoid identity theft on the dark web.
Identity theft: Scammers on the dark web might trick you into hasty purchases or disclosing personal information so they can collect your data and use it against you. Encrypt your connection and use pseudonyms and cryptocurrency to avoid identity theft on the dark web.
-
 Phishing: Due to the abundance of fake and dodgy websites, phishing remains a consistent problem on the dark web. Clicking on these fake websites could result in a computer virus that needs to be removed.
Phishing: Due to the abundance of fake and dodgy websites, phishing remains a consistent problem on the dark web. Clicking on these fake websites could result in a computer virus that needs to be removed.
-
 Keylogging: Keylogging software is designed to record the strokes of your keyboard leaving your passwords, credit card information, and other personal details potentially exposed. On the dark web, hackers may use keylogging software to try to steal valuable information from you.
Keylogging: Keylogging software is designed to record the strokes of your keyboard leaving your passwords, credit card information, and other personal details potentially exposed. On the dark web, hackers may use keylogging software to try to steal valuable information from you.
Threats are scattered all over the dark web, but there’s plenty you can do to protect yourself. Learning more about cybersecurity to boost your online protection is a great place to start.
The history of the dark web
The dark web was created not long after the first message was sent in 1969 over the original internet, ARPANET. Covert networks — or darknets — emerged quickly and provided users with private networks to communicate.
In 1989, Ian Clarke launched the Freenet project, which aimed to allow anonymous online interactions at a time when internet anonymity was difficult to achieve. Soon after, the Tor network was created as a safe and hidden way for American intelligence operatives to communicate with each other across the globe.
In 2008, the Tor Project launched the official Tor Browser, which is now the most popular way to access the dark web. The name Tor is short for The Onion Router, which refers to the way the TOR network routes internet activity through different overlay networks (like an onion’s layers) — each helping to encrypt the traffic between your computer and the internet.
Keep your data in the dark — and off the dark web
Regardless of why you may need to get on the dark web, protecting your connection and your data is crucial. AVG Secure VPN helps you conceal your IP address while encrypting your connection, keeping your activity more private. If you ever need to download and use Tor, a VPN will help prevent your ISP or anyone else from knowing about it.

















