What is a proxy server?
A proxy server is a computer that intercepts and manages traffic between two devices, networks, or protocols. Proxies are a gateway that act as an intermediary between your computer and the websites and internet services you’re using. They can serve as firewalls, filters, caches, or facilitate shared network connections.
That’s the general definition of a proxy server, which is also known as a forward proxy server. Although there are many types of proxy servers, each with varying functions, they all serve the fundamental task of representing you (acting as your proxy) as you navigate the internet.
What does a proxy server do?
A proxy server relays traffic between your device and the web, ensuring that your browser is never in direct contact with the sites you visit. When you send a web request, the request first goes to the proxy server. The proxy then sends your request on to the relevant web server and forwards the response back to your device.
Acting as intermediaries, proxies help protect your privacy and strengthen the security of your local network. Here are some other useful features of proxy servers.
-
Firewall & web filter abilities: you can restrict access to certain websites and protect your network from hackers.
-
Shared network connections: you can connect multiple devices under one network.
-
Data caching: you can increase browsing speeds by saving copies of websites.
How does a proxy server work?
A proxy server relays your internet requests out to their respective destinations, then fields the responses and passes them back to you. With a proxy server, the only point of contact between your device’s local network and the websites you’re visiting is the proxy server itself.
All proxy servers work with your computer’s IP address. An IP address functions like a home address for your computer or device. Just as mail is delivered to the physical address of your home, your internet requests are returned to your unique IP address, ensuring that data gets transmitted to the right location.
When you’re online without a proxy, your IP address is exposed for web servers and others to see. It’s incredibly easy to find your IP address, which may lead to security breaches and other identity-related issues. An online proxy also has an IP address, which is used on your behalf so that you don’t have to reveal your actual IP address.
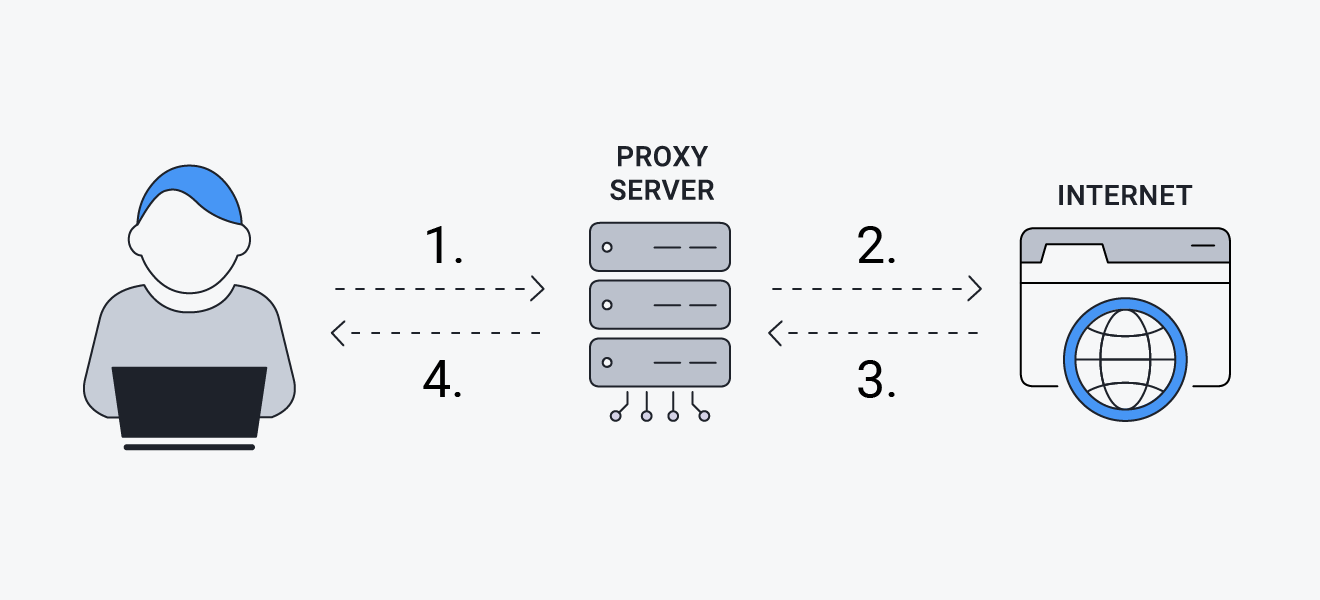 Step 1: Your web requests are sent from your IP address to the proxy server. Step 2: The proxy server passes your traffic to the website you want to visit, under a different IP address. Step 3: Responses from the website are sent back to the proxy server. Step 4: The proxy server passes the requested data back to you, without the website ever communicating directly with your device.
Step 1: Your web requests are sent from your IP address to the proxy server. Step 2: The proxy server passes your traffic to the website you want to visit, under a different IP address. Step 3: Responses from the website are sent back to the proxy server. Step 4: The proxy server passes the requested data back to you, without the website ever communicating directly with your device.
A web-based proxy server can mask your IP address, making it difficult for a web server to track your physical location. But hiding your IP address does not encrypt your internet traffic, meaning that your data requests — including your usernames, passwords, and other account info — are still vulnerable.
Set up and installation
Whether you use a Windows PC or a Mac, your computer has settings to help you set up a proxy server. Within the proxy settings, your operating system can often automatically detect a list of available proxy servers.
But it’s also possible to enter a proxy’s unique IP address and port number. That information should be given to you by your provider if you’re using a private or business proxy server. Find out more about how to find your proxy settings on your devices.
What are forward proxies?
Forward proxies send outgoing requests on behalf of an end-user or network. The forward proxy then receives the replies to those requests and passes them back to the proxy user. Forward proxies can be configured to evaluate, or screen, internet traffic and handle the requests based on specified criteria. For example, some outgoing requests may be blocked.
What are reverse proxies?
Reverse proxies receive client requests on behalf of a server or group of servers, then pass those requests on to the servers if needed. This prevents anyone from directly communicating with the servers while also improving performance via load balancing, where incoming traffic is spread across multiple servers rather than just one.
Types of proxy servers
While proxies all serve to represent you online, different proxy servers perform this task in different ways to meet your specific needs.
Transparent proxies
A transparent proxy tells web servers that it’s a proxy, and it passes along your actual IP address, effectively identifying you to the web server. A transparent proxy is not used for security or privacy purposes. Generally, transparent proxies are used by schools, businesses, and public networks like libraries for content filtering or data caching.
Distorting proxies
A distorting proxy gives a false IP address to the web server, though it still identifies itself as a proxy. The false address provides anonymity, but the true benefit is that you can trick the web server into thinking you’re in a different location. This is how distorting proxies can help you get around geo-based content restrictions.
Although distorting proxies add a layer of security, the downside is that some websites will automatically block their connections.
Anonymous proxies
An anonymous proxy will keep your IP address hidden from the websites you visit. This can help combat identity theft as well as allow for anonymous browsing. But anonymous proxies still reveal themselves as proxy servers, and some websites may not give you access.
High anonymity proxies
A high anonymity proxy will periodically change the IP address that it reveals to the web servers of the sites you visit. That makes it more difficult for websites to use online tracking techniques to snoop on your browsing. If cybersecurity is a concern, high anonymity proxies are the best proxy solution.
A high anonymity proxy also does not reveal itself as a proxy working on your behalf. That ensures that your digital tracks are covered, making it the most secure type of proxy server available.
Despite offering some degree of security, most proxy servers won’t encrypt your web traffic, leaving you vulnerable to online threats like hackers or snoops. A VPN (virtual private network) offers much more protection, especially if you want to stay secure on public Wi-Fi.
AVG Secure VPN masks your IP address so that you can browse the web freely, while securing your entire internet connection with advanced, military-grade encryption. With a VPN, you’ll stay anonymous online and keep your data safe, whenever you connect.
Why use a proxy server?
-
 Content oversight or filtering: Maybe you’re a business owner who wants to limit internet use in the office. Or maybe you’re a parent looking to restrict YouTube or other streaming access for your kids. A proxy server is a good tool for blocking certain content on your Wi-Fi network.
Content oversight or filtering: Maybe you’re a business owner who wants to limit internet use in the office. Or maybe you’re a parent looking to restrict YouTube or other streaming access for your kids. A proxy server is a good tool for blocking certain content on your Wi-Fi network.
-
 Privacy: Proxy servers make it difficult for web servers to track requests back to their origin (you and your network). This ensures that your browsing behavior and personal information are more secure, and that you enjoy a safer browsing experience.
Privacy: Proxy servers make it difficult for web servers to track requests back to their origin (you and your network). This ensures that your browsing behavior and personal information are more secure, and that you enjoy a safer browsing experience.
-
 Improved browsing speeds and bandwidth savings: If you or your organization frequently use certain websites, a proxy can save a copy of these sites onto its server — this is called caching. Once saved, your browser can directly access the website from your local server rather than having to go all the way back to the web server itself. Caching websites on a proxy server allows sites to load faster while conserving bandwidth.
Improved browsing speeds and bandwidth savings: If you or your organization frequently use certain websites, a proxy can save a copy of these sites onto its server — this is called caching. Once saved, your browser can directly access the website from your local server rather than having to go all the way back to the web server itself. Caching websites on a proxy server allows sites to load faster while conserving bandwidth.
-
 Access blocked content: There are a number of ways to unblock websites and a proxy is one of them. By concealing your actual location, proxy servers can help you bypass content restrictions set up by employers, governments, or other censors.
Access blocked content: There are a number of ways to unblock websites and a proxy is one of them. By concealing your actual location, proxy servers can help you bypass content restrictions set up by employers, governments, or other censors.
-
 Proxy servers can unlock access to blocked websites. Rather than a request getting blocked by a firewall, it gets relayed through a proxy server, bypassing the filter and unlocking the content.
Proxy servers can unlock access to blocked websites. Rather than a request getting blocked by a firewall, it gets relayed through a proxy server, bypassing the filter and unlocking the content.
Who uses proxy servers?
Businesses, schools, libraries, and other organizations with public networks often use proxy servers to block certain sites or filter content on their network. Offices or other workplaces also use proxy servers to streamline performance and save bandwidth, because proxies can cache frequently visited websites.
A sports fan can use an online proxy to root for their home team when they’re traveling abroad. And citizens of repressive countries who want access to a free internet can bypass government censors and other content restrictions with the help of a proxy server.
Proxy servers are great tools that offer control, privacy, efficiency, and access to otherwise blocked content.
What is a proxy server on PS4?
Gamers often configure proxy servers on PlayStation 4, PlayStation 5, or other devices for an enhanced gaming experience. This allows all gaming data to be channeled from the gaming server through an optimized proxy server to the PS4 console, meaning increased uptime and connection speeds, and reduced lag and buffering.
How to find the proxy server address
If you need to find your proxy server address on Windows, Mac, or your phone, here’s how:
How to find your proxy server address in Windows
-
Open Settings from the Start menu.

-
Click Network & Internet.

-
Choose Proxy from the menu on the left. If your computer is connected to a proxy, you’ll see the proxy address here.

How to find your proxy server address on Mac
-
Open the Apple menu and click System Preferences.

-
Click Network.

-
Select Ethernet or Wi-Fi, then click Advanced.

-
Select the Proxies tab.

-
Select the type of proxy you’re using to see the proxy address.

How to find your proxy settings on Android
The following steps for finding Android proxy settings apply to a Samsung phone. Steps for other phones may differ slightly.
-
Open Settings, tap Connections, then tap Wi-Fi.

-
Tap the settings cog next to the network you’re connected to.

-
Scroll down and tap to expand the Advanced dropdown menu. If you’re using a proxy server, it will be visible here.

How to find your proxy settings on iOS
-
Open Settings and tap Wi-Fi.

-
Tap the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.

-
Scroll down and tap Configure Proxy. If your phone is using a proxy, you’ll see the info here.

Proxy server risks
-
 Potentially unstable: When people crowd onto free web proxies, you may experience service disruptions as the server struggles to sustain simultaneous connections.
Potentially unstable: When people crowd onto free web proxies, you may experience service disruptions as the server struggles to sustain simultaneous connections.
-
 Slow speeds: Does your internet connection seem slow? Crowded proxies may have speed issues. And because your traffic is going through an extra step on its journey through the internet, your connection may feel slower than usual.
Slow speeds: Does your internet connection seem slow? Crowded proxies may have speed issues. And because your traffic is going through an extra step on its journey through the internet, your connection may feel slower than usual.
-
 No encryption: Most proxy servers don’t encrypt your web traffic, which means your personal data can be exposed or stolen.
No encryption: Most proxy servers don’t encrypt your web traffic, which means your personal data can be exposed or stolen.
-
 Free proxy server risks: Free proxies may generate revenue by secretly tracking your behavior and selling your data and online activity to advertisers.
Free proxy server risks: Free proxies may generate revenue by secretly tracking your behavior and selling your data and online activity to advertisers.
-
 Malware exposure: Some free proxies are actually traps designed to lure in unsuspecting users, then redirect them to malicious websites or display malvertising ads.
Malware exposure: Some free proxies are actually traps designed to lure in unsuspecting users, then redirect them to malicious websites or display malvertising ads.
-
 Browsing history logs: Make sure any proxy you’re using does not log your online activity.
Browsing history logs: Make sure any proxy you’re using does not log your online activity.
There are many performance and security-related risks with proxy servers. AVG Secure VPN is a secure and safe way to hide your IP address, conceal your online activity, and enjoy a fast and stable connection whenever you want to browse the web privately.
What are the alternatives?
If cybersecurity is important to you, the risk of using a proxy server may be greater than the reward. When comparing a proxy to a VPN, you’ll see significant benefits to using a VPN instead.
Proxy servers and VPNs use remote servers to connect you to the internet. Both can protect your IP address, and both proxies and VPNs can conceal your location.
The main difference is that a VPN will fully encrypt your internet traffic and data for enhanced cybersecurity anywhere you go online.
Use a trusted VPN for true privacy and anonymity online
With e-commerce, social media, online banking, and all the other online services out there, your identity and personal data are at risk of exposure on multiple fronts. While proxy servers provide a good first line of defense, to protect your data and compete with the variety of threats out there, you need a VPN.
AVG Secure VPN offers all the benefits of a proxy server along with military-grade encryption, ensuring that your data and privacy remain fully protected. And with servers all over the world, you’ll enjoy world-class protection wherever you are — and blazing-fast connection speeds.
/What_is_a_proxy_server-Hero.jpg?width=1200&name=What_is_a_proxy_server-Hero.jpg)
 Step 1: Your web requests are sent from your IP address to the proxy server. Step 2: The proxy server passes your traffic to the website you want to visit, under a different IP address. Step 3: Responses from the website are sent back to the proxy server. Step 4: The proxy server passes the requested data back to you, without the website ever communicating directly with your device.
Step 1: Your web requests are sent from your IP address to the proxy server. Step 2: The proxy server passes your traffic to the website you want to visit, under a different IP address. Step 3: Responses from the website are sent back to the proxy server. Step 4: The proxy server passes the requested data back to you, without the website ever communicating directly with your device. Proxy servers can unlock access to blocked websites. Rather than a request getting blocked by a firewall, it gets relayed through a proxy server, bypassing the filter and unlocking the content.
Proxy servers can unlock access to blocked websites. Rather than a request getting blocked by a firewall, it gets relayed through a proxy server, bypassing the filter and unlocking the content.



























